Contact us
When replacing quenching baths in the hardening shop, there are two cost-intensive challenges: Wastewater containing salt must be disposed of at high cost, and the salt that is lost due to salt carry-over must be added at high cost. The innovation team of H2O GmbH has therefore developed a new technology for vacuum distillation that enables a double circulation for both water and salt. This considerably reduces disposal and operating costs.
An essential process for influencing material properties is the hardening and subsequent tempering of steel or other alloys. Hardening focuses on achieving a hard, wear-free surface, while tempering and quenching aims to increase the strength of the treated material. Heating to temperatures of more than 700 °C and subsequent cooling (quenching) induces different crystal structures in the metal that can influence its physical properties. To achieve rapid cooling, the materials are exposed to different quenching media. Depending on the material to be treated, pure water with appropriate additives, oils or salt baths can serve as suitable media.
Since various impurities concentrate in these baths, quenching solutions must be replaced after a certain service life. In addition, saline rinsing water accumulates when the quenched parts are cleaned afterwards. This process wastewater must be disposed of at high cost.
Salt deposits adhering to the workpieces result in the problem that after a certain time, a considerable amount of salt is removed from the process by carry-over and must be replenished. This is also a cost-intensive effect.
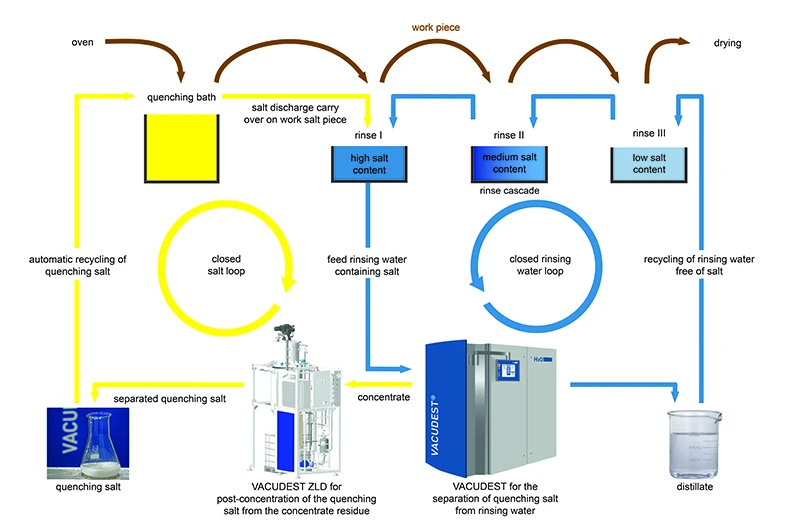
Thanks to vacuum evaporation, a dual purpose cycle can be implemented at this point. By separating water and salt due to different boiling points, clean water is obtained by distillation, which can be reused again for cleaning the parts in a process-oriented manner. This is the first recirculation. Alternatively, if the water must be discharged into the sewer, all official consent limits can be met.
The second cycle is made possible with the help of an additional salt drying module. The saline, still liquid concentrate from the VACUDEST can be further treated by the new VACUDEST ZLD technology. The VACUDEST ZLD is a post-concentrator developed precisely for applications where the aim is to minimize evaporation residues or dry them to completion. Through efficient energy recycling, the residual water content is reduced up to 20 percent with almost no external energy input. The energy consumption is less than 150 kWh/m³, which is almost completely provided by the waste heat of the VACUDEST. At the end of the cycle, the concentrate is finally conveyed out of the VACUDEST ZLD. During cooling, the solubility limit of the dissolved salts is often exceeded and the salt crystallizes out. When recovered, valuable salt can be returned to the salt bath.
By recycling the distillate as rinsing water and recycling the hardening salt, dual-purpose circulation is implemented and disposal as well as operating costs can be reduced considerably. In general, the investment in this system often pays for itself in less than two years.

Saving disposal and operating costs: The VACUDEST vacuum distillation system (left) enables the water to be recirculated, while the VACUDEST ZLD technology (right) recovers the hardening ice salt. The ZLD technology is available for a wastewater volume starting from 1000 m3/year.
You want to be part of our team and create the wastewater-free future with us?
We will tell you how!
Your contact is:
Bettina Böhringer
Human Resources
+49 7627 9239-201
career@h2o-de.com
You have questions on our VACUDEST systems?
Kindly contact us!
Your contact is:
Thomas Dotterweich
Senior Sales Engineer
+49 7627 9239-306
thomasm.dotterweich@h2o-de.com
You need consumables, spare parts or a maintenance date?
We will be pleased to assist you!
Your contact is:
Carles Fité
Technical Customer Support
+49 7627 9239-888
carles.fite@h2o-de.com