Contact us
Vacuum distillation reliably and gently separates substances with different boiling points. The function of the vacuum is to lower the boiling temperature, allowing the water in the industrial wastewater to be evaporated in an energy-saving manner.
All substances with higher boiling points, such as oils, fats, heavy metals, salts, or surfactants remain in the evaporation residue.
For a vacuum distillation process to run reliably and for the separation process to deliver high-quality results, it is important that the vacuum in the evaporator is meticulously maintained.
This places high demands on the vacuum pumps as well as on vacuum control and the choice of the correct, high-quality pump is a very important factor in a vacuum evaporation plant. Depending on the application, different vacuum pumps are used.
Depending on the application, different vacuum pumps are used. Read about the different types of pumps, their applications, as well as their specific advantages and disadvantages:
The diaphragm pump moves gases and liquids by a displacement mechanism. This involves moving a rubber or thermoplastic diaphragm in a cavity whose inlet and outlet are closed by a shut-off valve.
These valves can be flap valves, butterfly valves or check valves, depending on the application. The diaphragm of the pump is bent, which causes the volume in the chamber of the pump to expand or contract.
If the volume is increased, the pump will prime; if the volume is decreased, the material being pumped will be forced through the discharge valve. All diaphragm pumps provide a hermetic seal between the mechanism that bends the diaphragm and the chambers through which the substances to be pumped are conveyed.
This allows pumping, compression and evacuation without lubrication. These pumps, with the selection of the right diaphragm material, can cover a very wide range of pressures and temperatures.
Diaphragm pumps are also able to handle highly viscous fluids, slurries, and fluids with high levels of solids, such as sand, making diaphragm pumps well-suited for applications in the oil refining or water treatment industry. In contrast to other vacuum pumps (e.g. water jet pumps), diaphragm pumps have a relatively high purchase price, but can offer almost maintenance-free operation and a high efficiency of up to 97%. Also, in contrast to water jet pumps, no wastewater is generated during the operation of diaphragm pumps.
Water jet pumps are frequently used for the suction of liquids or gases. These pumps use a liquid as the propellant. Through a nozzle, the propellant is strongly accelerated and a negative pressure is created. The negative pressure then sucks the liquid from the suction water tank. This can also entrain some solids.
Water jet pumps are often used in chemical laboratories. They have a very simple and reliable way of operation as well as a low initial price.
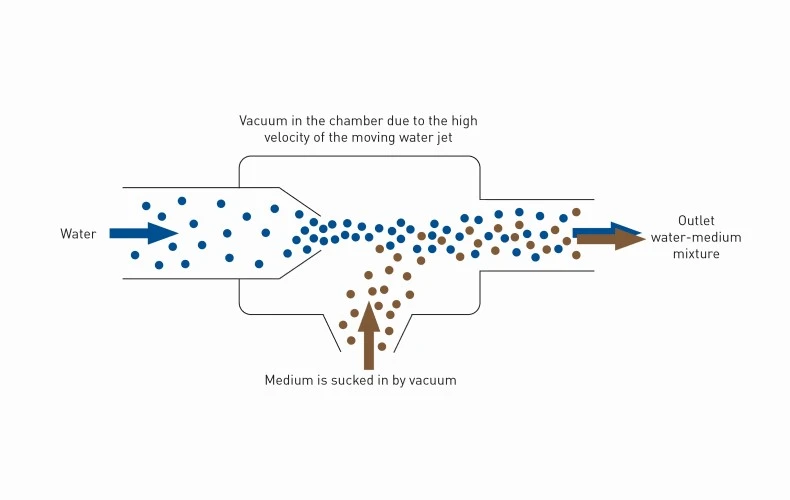
The water jet is strongly accelerated by forcing it through a nozzle. A vacuum is created sucking in the medium to be pumped out.
The dry screw vacuum pump gets its name from the fact that its operation does not require any liquids that could contaminate the pumped material. Two screw rotors rotate in opposite directions and enclose the pumped medium between them. The movement compresses it and transports it successively to the discharge side. The pump can produce a very high vacuum without the need for multiple stages.
Most commonly, these pumps are used in industries that require care to keep gases and vapors free of any contaminants. This is the case, for example, in chemical and petrochemical applications , where they are used to pump volatile organic compounds, or in waste processing, where they are used to remove waste gas from landfills to reduce environmental pollution.
Due to its design, the pump can be used with many gases, especially those that have a high particle density. The dry screw vacuum pump is highly resistant to corrosion.
Its high efficiency is a key feature that ensures that the pump has a long service life, and the uniform temperature distribution also reduces punctual thermal stress.
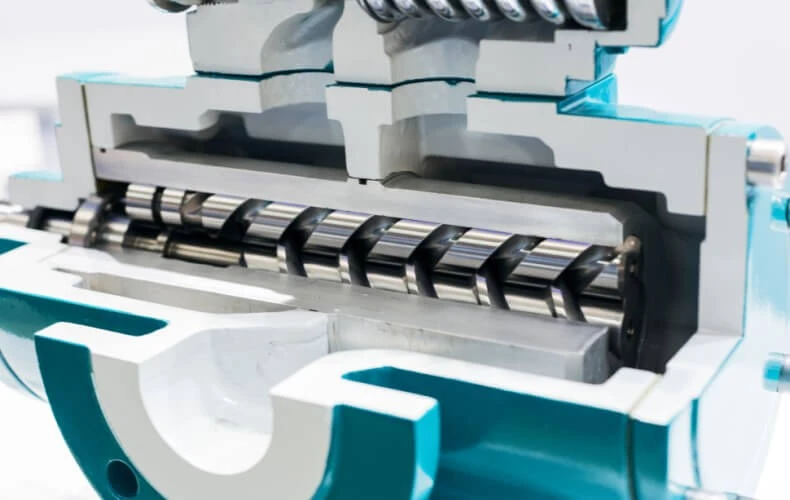

The liquid ring vacuum pump is a very robust pump and is used in various subsections of a vacuum distillation. Depending on the application, single-stage or two-stage pumps are used.
The liquid ring vacuum pump gets its name from its operating principle: the pump has an eccentrically mounted impeller and is partially filled with an operating liquid. When the pump is in operation, the centrifugal forces cause a so-called liquid ring to form in the housing.
The pumped liquid is transported in the spaces between the vanes and the liquid ring. Due to the eccentric mounting of the impeller, these gaps become smaller and smaller and the pumped medium is compressed before it is discharged through an outlet in the center of the impeller.
The heat of compression is transferred to the liquid ring during this process. A constant exchange of operating liquid ensures constant and optimum cooling.
The liquid ring vacuum pump is a safe and reliable pump for handling contaminated and potentially dangerous gases as operation is very simple and there are no parts in contact with hazardous material.
Note: The disadvantages of this pump are the fact that the pumped gas is mixed with the service liquid, as well as a high-power consumption due to internal friction losses. Therefore, these pumps are not suitable for H2O VACUDEST systems.
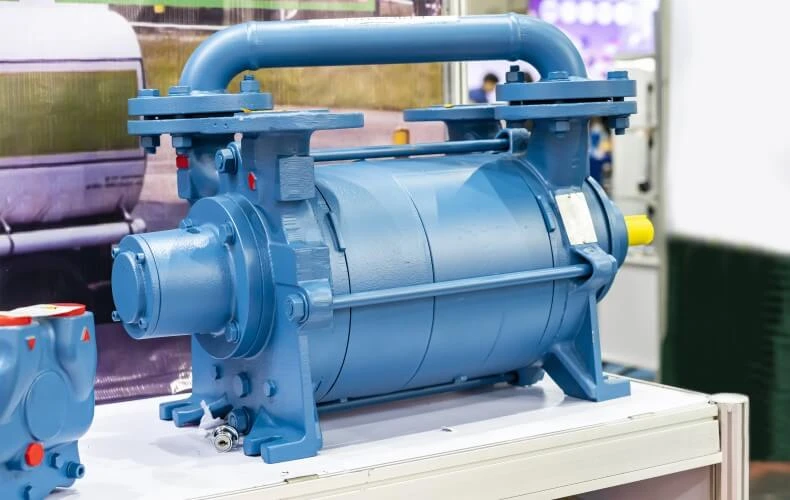

Rotary vane vacuum pumps operate in almost the same way as liquid ring vacuum pumps - except that only the positioning of the rotator provides the volume differences, and no water is used. Similar to the liquid ring vacuum pump, the interior of rotary vane pumps is divided into different chambers which change their volume during rotation. In this case, the rotary vane is embedded in the rotary body with springs and presses against the inner wall of the hollow cylinder during rotation.
To minimize wear on the pump, which is quite high for this pumping technology, there is a necessity for the use of a lot of lubricant. The use of lubricants is a clear downside of this pump since it also contaminates the material being transported.
Major advantages of rotary vane vacuum pumps are, that they are very efficient, very cost effective and have a controllable flow rate that works in both flow directions.
Rotary vane vacuum pumps are particularly well-suited when high suction capacities are required and when they are operated in an environment, where oil or other chemical substances may also be present.
Good to know: At H2O we want to remove foreign substances from the water in vacuum evaporators. Therefore, rotary vane vacuum pumps are not suitable for our use. Instead, our vacuum distillation systems are equipped with a roots pump.

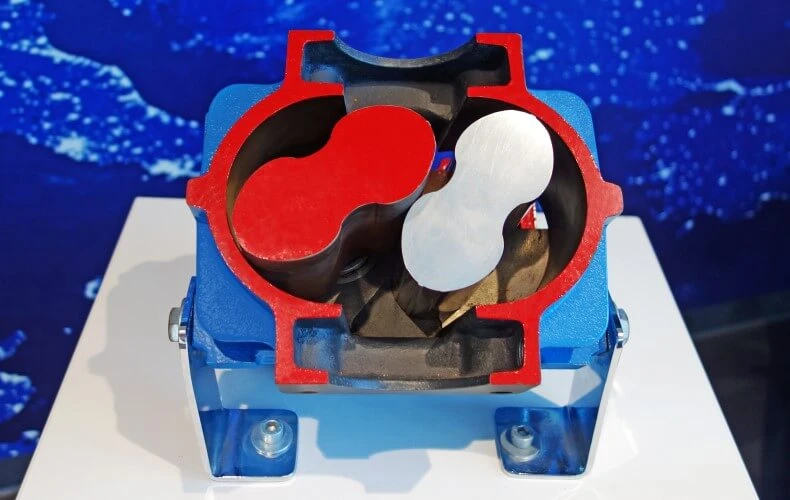
It consists of a housing with 2 symmetrical rotary pistons. The pistons have two or three lobes and rotate in opposite directions in the housing. The rotation of the pistons causes the medium to flow into the housing.
The pistons transport the medium through the pump. Compression is achieved by the backpressure of the gas already conveyed.
The energy consumption of the two-lobe rotary blowers is - in comparison to the already very economical three-lobe blowers - again significantly lower.
Two-lobe blowers are used primarily where maximum economy is required and gas volume pulsations do not result in any disadvantages. In addition, the two-lobe block is less sensitive to particle contamination of the air intake.
Roots pumps are very effective, especially at low vacuum, and are therefore widely used in many industrial applications such as vacuum distillation, vacuum drying and vacuum packaging.
Find out more about the advantages of H2O VACUDEST systems with integrated roots pumps.

You have questions on our VACUDEST systems?
Kindly contact us!
Your contact is:
Thomas Dotterweich
Senior Sales Engineer
+49 7627 9239-306
thomasm.dotterweich@h2o-de.com
You need consumables, spare parts or a maintenance date?
We will be pleased to assist you!
Your contact is:
Carles Fité
Technical Customer Support
+49 7627 9239-888
carles.fite@h2o-de.com
You want to be part of our team and create the wastewater-free future with us?
We will tell you how!
Your contact is:
Bettina Böhringer
Human Resources
+49 7627 9239-201
career@h2o-de.com